

Some instruments use a band-pass filter and others a second monochromator on the emission side. In the spectrofluorimeters, a monochromator selects the excitation wavelength from the band spectrum of either a xenon lamp or a deuterium lamp. It is distorted by the A sensitivity of the emission detection system. A m) should be similar in shape to the spectrum of the xenon lamp. This spectrum designated F],(A) = Fmm (A x. Record the spectral light signal between 250-600 nm vrith both monochromators scanning synchronously. The two curves thus generated can be compared and the correction fector curve, C(X), calculated. Often neutral density filters will have to be placed in the emission beam in order to prevent signal saturation of the PMT. This spectrum is a close representation of the true xenon lamp intensity profile. Then ExM is scanned from 250-600 nm and the spectrum is recorded. A red cut-oflf filter is placed in front of the entrance slit to EmM and Xem is set to 620 ran. This is a similar configuration to the cell in the reference channel of the instrument. The cuvette is oriented so that the hypotenuse is on the face opposite to EmM. The reflector is replaced by a concentrated sample of rhodamine B in a triangular cuvette. This will produce a spectrum of the xenon arc source that has been distorted by the sensitivity variation of the emission detection system. In this method a diffuser plate or an MgO scatterer plate is placed in the sample holder and then both ExM and EmM are scanned synchronously from 250-600 mn. Ī method that has shown to be quite satisfactory and relatively straightforward is described in Protocol 2. The spectrum of a low-pressure Hg lamp is presented in Fig. Mercury lamps under high pressure can be used to provide a continuum, but low-pressure Hg lamps, which emit a line spectrum, are often used with filter fluorometers. The emission spectrum of a xenon arc lamp is shown in Fig. This lamp emits a continuum from 200 nm into the IR. The quartz envelope is filled with xenon gas, and an electrical discharge through the gas causes excitation and emission of light. A schematic of a xenon arc lamp is given in Fig. range shows that homogeneity is sufficient for measuring second-order rate constants (14). Īn approximate calculation taking into account the measured absorption spectrum of 0.001M NaOH solution and the relative spectral emission of the xenon lamp in the useful 185-220-nm. While common mercury xenon lamps still produce significant mercury emission bands, especially in the UV region, the smoother xenon lamp spectrum finds application in environmental photochemistry experiments because of its resemblance to solar radiation (Figure 1.1). The spectral lines are broadened due to the high pressure and temperature and they are superimposed on a continuous background of radiation (Figure 3.4). The most intense sources of UV radiation are the high-pressure ( 100 bar) mercury arcs. The Weather-Ometer was operated with the lamp on continuously and the exposure chamber was maintained at a black panel temperature of ll+5 5☏ and a relative humidity of 30 5. 77 +0 horosilicate inner and outer filters was used as a laboratory light source because its emission spectrum is similar to that of sunlight, as illustrated in Fig. Ī 6000W xenon arc Atlas Weather-Ometer (] ) equipped with Corning No.
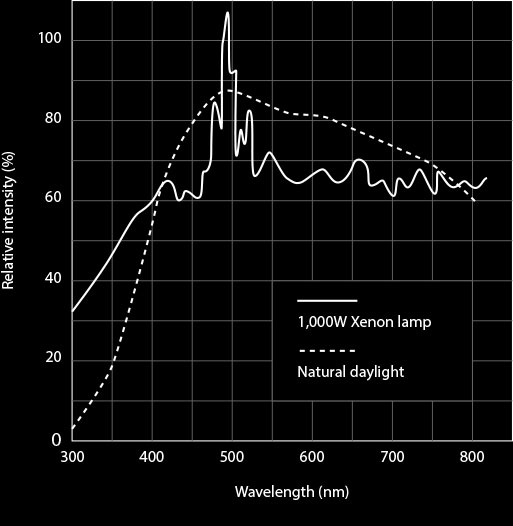
Common lamp sources in commercial fluorometers include xenon lamps for excitation from the UV to the near-IR (250 nm to llOOnm). The simplest steady-state measurements of fluorescence properties such as the fluorescence emission spectrum or the steady-state anisotropy can be carried out in a standard fluo-rometer with excitation from a lamp source and a monochromator. It has two monochromators and two filters, for both the excitation and emission modes and can be operated either in double-beam ratio or single beam. This particular instrument is equipped with a Xenon lamp that emits a continuous spectrum of wavelengths. A more sophisticated instrument is the Farrand VIS-UV Chromatogram Analyser CFigure 3) that can also be used to measure the fluorescence spectra as well as to obtain reliable quantitative data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
